What is Hyperledger?
The most important thing to recognize about Hyperledger is that it is NOT A COMPANY, NOT A CRYPTOCURRENCY, and NOT A BLOCKCHAIN--which is why it does not support Bitcoin or any other cryptocurrency.
Instead, Hyperledger is a “hub” or umbrella project for open industrial blockchain development, created by The Linux Foundation in December 2015. The platform’s first founding members were announced a year later, in February 2016, with ten more members joining a month later. It quickly grew to over 100 members, including IT-companies like IBM, Fujitsu, SAP, Huawei, Nokia, Intel, and Samsung.
Other members include financial institutions like American Express, J.P. Morgan, BBVA, Wells Fargo, among others. Blockchain startups like Consensys and Blockstream are also in the mix.
In September 2020, it added eight new organizations, including Chainstack, SIMBA Chain, SIX Digital Exchange, and Visa.
How It Works
Cardano uses the “Ouroboros” model alongside its Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. For those individuals, or validators, who want to help validate transactions, they are required to freeze a certain amount of ADA coins, establishing their “stake” in the system. Once a validator helps verify a transaction, they receive additional ADA coins as their reward.
The higher their stake, the higher likelihood a validator has of receiving their reward.
What is “Ouroboros?”
While there are many other PoS blockchains out there, Cardano sets itself apart because of its claim that they offer an actual, true random way of selecting a validator. This, according to the developers is why they built their Ouroboros protocol on top of the standard PoS model.
Ouroboros uses stake as the primary resource to identify the leverage participants have in the system. As it requires very little physical resources to run, Cardano is considered to be extremely environmentally friendly.
The protocol also guarantees the dynamic availability a PoW system never could. In other words, it continues to operate, according to Kiayias, even if an arbitrarily large number of participants decide not to stake and maintain the ledger.
The process of joining and participating in the protocol, according to Kiayias, doesn’t require the availability of any special shared resource such as a checkpoint. When engaging in the protocol requires nothing more than the public genesis block of the chain and access to the network, it eliminates the point of failure that is a trusted shared resource.
Many believe Ouroboros to be a game-changing protocol.
Source: Blockonomi
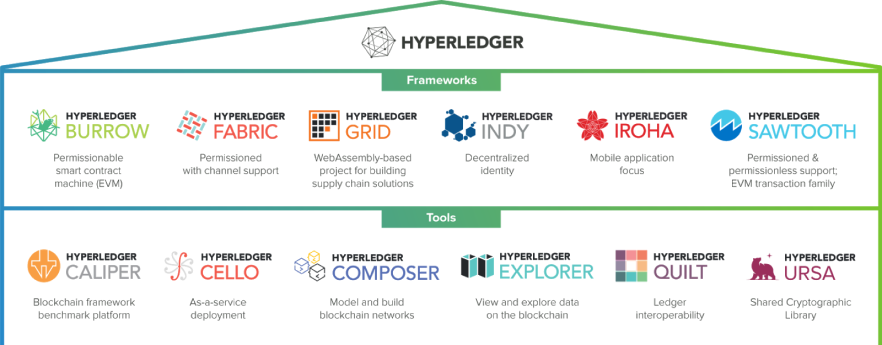
Hyperledger’s infrastructure enables businesses to apply various modular blockchain solutions and services to help improve operations and increase efficiency.
The hub’s infrastructure can be broken down into modular frameworks and modular tools.
Since it’s not an organization, crypto network, or blockchain system, it simply provides the necessary architecture and infrastructure which develop enterprises develop blockchain-based systems and applications for industrial use. Let’s explore each.
Cardano uses the “Ouroboros” model alongside its Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. For those individuals, or validators, who want to help validate transactions, they are required to freeze a certain amount of ADA coins, establishing their “stake” in the system. Once a validator helps verify a transaction, they receive additional ADA coins as their reward.
The higher their stake, the higher likelihood a validator has of receiving their reward.


#1 - Hyperledger BURROW
Burrow is a modular blockchain framework with a permissioned smart contract engine. It was originally developed by Monax to assist Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), in part. Burrow essentially handles transactions and executes smart contract code on EVM.
The framework uses Tendermint Proof-of-Stake BFT consensus engine, and can use its Application Blockchain Interfact (ABCI).
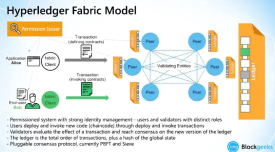

#2 - Hyperledger FABRIC
Hyperledger Fabric is a platform that implements an entirely new architecture, using the “execute-order-validate-architecture”, which allows transactions to execute before the blockchain reaches consensus on their place in the chain. This helps address issues including resource exhaustion, performance attacks, and other security issues.
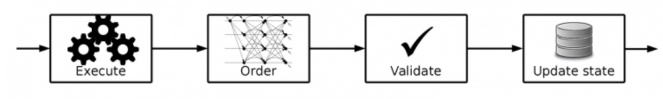
The transaction flow in Hyperledger Fabric, in which transactions are executed and endorsed first, before ordering them and validating that they do not conflict | Source: IBM
Unlike the traditional order-execute paradigm, Fabric’s new architecture is a radical change that separates the transaction flow into modular building blocks and includes elements of scalable replicated databases. In plain, Fabric created a hybrid that combines passive and active replication.

Figure 1: The traditional architecture for building blockchains and resilient replicated services, where transactions are ordered first and executed later | Source: IBM
In this system, “passive” refers to every transaction executed or endorsed by only a subset of peers, allowing for parallel execution and non-determinism.
“Active”, refers to Fabric’s policy on respecting application-specific trust assumptions according to the transaction endorsements--meaning that the transactions don’t have to be constructed in all one order, so long as they are consistent and come together at the right time.
#3 - Hyperledger INDY
INDY is another modular framework and distributed ledger which is explicitly built for “decentralized identity management”. The server portion of Indy-node is built in Python, while the Indy-SDK is written in Rust.
This comes with tools and reusable components that offer privacy features such as self-sovereignty, privacy, and verifiable claims.

#4 - Hyperledger IROHA
IROHA is a blockchain framework written in C++ that helps facilitate mobile application development. It was developed by several leading Japanese tech companies, including Hitachi.
It runs off a new chain-based BFT consensus algorithm called Sumeragi.
Iroha comes in handy when managing digital assets, identity, and serialized data. Applications include interbank settlement, central bank digital currencies, payment systems, national IDs, and logistics.
#5 - Hyperledger SAWTOOTH
Sawtooth is a modular framework written in Python for running distributed ledgers. It can be subdivided into Sawtooth-raft and Sawtooth-sabre, both of which are written in Rust.
The framework incorporates Javascript and Go components, dynamic consensus, Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET) Consensus, parallel transaction execution, and private transactions.
Recently, the Sawtooth blockchain platform has integrated IoT sensors to improve seafood supply chain traceability. By attaching IoT sensors to fish tanks, all telemetry parameters including location, temperature, and humidity are recorded on the blockchain. This provides consumers with full access to complete records.
Modular Tools
#1 - Hyperledger Caliper
Caliper is a blockchain benchmark tool that is used to evaluate the performance of a specific blockchain implementation.
#2 - Hyperledger Cello
The project, “Cello”, helps create, manage, and terminate blockchains. It is a blockchain provision and operation system (think Windows OS or MacOS), helping to manage the lifecycle of blockchain networks. This also can be described as BaaS, allowing blockchain to be used through an on-demand “as-a-service” deployment model.
#3 - Hyperledger Composer
Hyperledger Composer is an application development framework which serves as a set of open-source tools that allows business owners, operators, and developers a way to create blockchain apps and smart contracts. This is a perfect example of Blockchain-as-a-Service (“BaaS”).
In 2020, Composer was combined into Hyperledger Fabric v1.4, which helps simplify and expedite Fabric-created blockchain applications. Prior to combining with Fabric, Composer was rendered inactive, as there were no new features or support provided, It’s built-in Javascript,
#4 - Hyperledger Explorer
Explorer is an open-source utility module, written in Javascript, that allows users to create a user-friendly web-based application, for purposes of blockchain deployment. This can be integrated with other authentication platforms, which of course supports the Hyperledger Sawtooth framework.
What’s the Industry Saying?
Behlendorf, the company’s executive director, believes that as enterprise blockchain adoption continues to accelerate, Hyperledger’s members will be a driving force for critical new technologies and solutions.
He references Chainstack, SIMBA Chain, SIX Digital Exchange, and Visa as “important new voices as [it] sets agendas and roadmaps that will keep pushing this market forward in the year ahead”.