Web 3.0: A New Digital Age?
Bitcoin was the opening act, setting the stage for Web 3.0 to come into effect. The philosophy behind Web 3.0 is that any given website’s algorithm is capable of learning user preferences and becoming more intelligent. In other words, online applications and websites would be capable of receiving information that’s on the Web, and provide its users with new information/data.
The Evolution of “The Web”
The Web can now be divided into three phases--Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and now Web 3.0.
The illustrations below help contextualize this timeline:
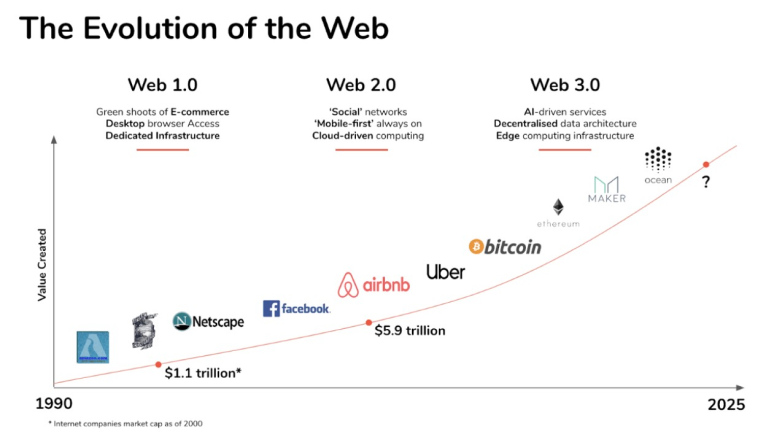
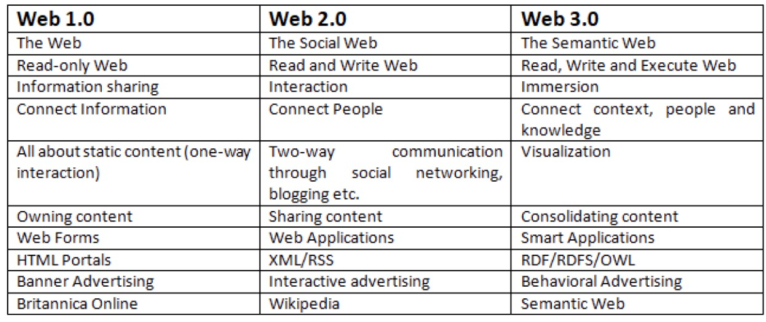
Source: Hacker Noon
The Semantic Web
Gian Gonzaga, Ph.D, eHarmony’s Senior Director of R&D, describes Web 3.0 as a web which learns and understands who you are, and gives you something back. The term “Web 3.0” was originally coined by Tim Berners-Lee, who referred to it as the Semantic Web. Berners-Lee initially envisioned the Semantic Web as one “in which computers become capable of analyzing all the data on the Web --the content, links, and transactions between people and computers”. It would be a leap forward to an open, trustless, and permissionless network”.
Where Web 2.0 was fueled by the birth and expansion of mobile, social media, and cloud computing, Web 3.0 is primarily based upon edge computing, decentralized data networks, and artificial intelligence. Its predecessor basically commoditized personal computer hardware, which was repurposed in data centers.
What Web 3.0 will hope to accomplish is taking user data and placing it within the grasp of users, supplementing these larger data centers with a multitude of computing resources on what can essentially be described as a peer-to-peer network. To put it plainly, when Web 3.0 is in effect, we will see less *hopefully* Congressional interference with our tech giants, as Facebook, Twitter, Google, and Apple will have no control over user’s data.
The Two Cornerstones
The two cornerstones of Web 3.0 is A.I. and Semantic Web, whereby Semantic Web will help teach the computer what the data means and that will evolve A.I. that can utilize that information.
What Does the 3.0 Landscape Look Like?
As of November 2020, DApps/wallets/platforms, privacy-centric internet browsers, and advanced cloud-based storage make up Web 3.0.
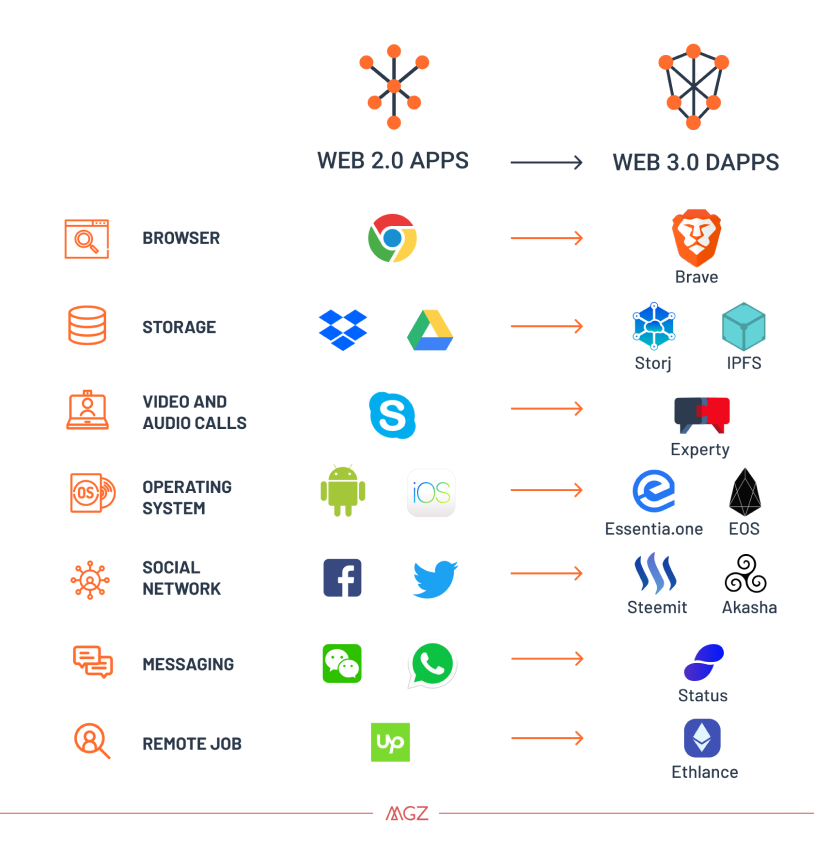
Source: HackerNoon
Advantages to Adoption
Web 3.0 serves to remove the middleman when it comes to data management. The best example is Ethereum, a decentralized platform, where no entity will be able to alter the code without the permission of other entities in the network.
By placing data back into the hands of users, ultimately, it will work to reduce the number of data breaches , as the platform would be decentralized and distributed. This would provide for the continuous flow of accurate information--something our era of “misinformation” could use.
And lastly, today’s applications are limited to the operating system (OS) they were designed for, placing a great deal of limitation on the potential market adoption. With Web 3.0 in effect, applications would be device-agnostic, capable of running on any type of device and customizable.
Challenges
Putting the rainbows aside, Web 3.0 also comes with its challenges, like having to deal with a huge input of data and providing the correct visibility the market and industry needs to understand and implement it.